|
Requests from outside of my district will be denied.
Assignments
Presentations
Unit 9 VocabularyHelpful LinksVideos |
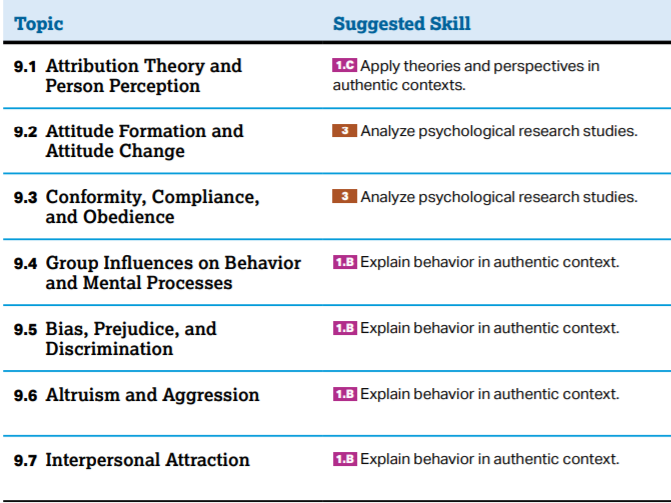
Unit 9: Social Psychology
AP Exam Weighting: 8-10% In this final unit, psychological concepts and theoretical perspectives are pulled together from throughout the course. Social psychology is the study of how other people and groups influence behavior and mental processes as well as how behavior and mental processes influence our experiences in social situations. Social psychology also involves the study of how our perceptions of social situations impact how we interact with others and how others interact with us. Social psychologists may focus on one aspect of social situations or interactions and may do so from a variety of theoretical perspectives, including other integrative perspectives. Course Skills: As the course nears completion, students should be able to describe and explain behavior and mental processes within the context of social psychology. As they learn new social psychology theories, students will build on their knowledge of psychological theories in general. These theories specifically build on the biological, cognitive, and sociocultural theories discussed in earlier units. The history of social psychology is filled with studies that are no longer considered ethical. Through these missteps, students will learn how to conduct valid research, identify ethical flaws, and use appropriate data and data collection processes. Preparing for the AP Exam: Students often have difficulty using social psychology key terms and phrases correctly to answer questions posed as scenarios. Common examples of interchanged behaviors include conformity, obedience, and compliance. Students often struggle to provide the depth or breadth required to show mastery of the content. Teacher can provide opportunities for students to work with scenarios related to social settings and interactions. Students should give general characteristics of the behaviors associated with interactions and common responses to social stimuli. When the scenarios involve a certain type of research, students should be expected to define the method and write accurately about validity, ethics, and outcome. |